
The hippocampal head is separated from the amygdala (5) by the uncal recess of the lateral ventricle (7) and is characterized by small digitations separated by small sulci, the digitationes hippocampi (6). The hippocampal head is the only portion of the hippocampus not covered by the choroid plexus (7). The head (1) is located in front of the mesencephalon, the body (2) can be found at the level of the mesencephalon and the tail (3) is posterior to the mesencephalon. To easily recognize the different portions of the hippocampus, we can use the mesencephalon (4). 1 = hippocampal head, 2 = hippocampal body, 3 = hippocampal tail, 4 = mesencephalon, 5 = amygdala, 6 = hippocampal digitations, 7 = temporal horn of the lateral ventricle, 8 = uncal recess of the lateral ventricle, 9 = splenium of the corpus callosum, 10 = subsplenial gyri, 11 = crura of the fornices. FreeSurfer is a tool to quantify cortical and subcortical brain anatomy. The temporal lobe is composed of five convolutions: T1, T2. This study used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to investigate cortical volume.

The hippocampal body is shown in detail in Fig. 2. The hippocampus comprises the Dentate gyrus (DG), the cornus ammonis (CA) and the subiculum (sub). Zoomed-in 3-T coronal T2-weighted images at the level of the hippocampal head ( c) and the hippocampal tail ( d). Clinical information is often necessary to come to a correct diagnosis or an apt differential.ĭementia Epilepsy Herpes simplex encephalitis Hippocampus MRI.Īnatomy of the hippocampal formation on 3-T axial T2 ( a) and sagittal 3D-MPRAGE images ( b).Pathologic conditions centered in and around the hippocampus often have similar imaging features.Refractory epilepsy and dementia are the main indications requiring dedicated hippocampal imaging.Knowledge of normal hippocampal anatomy helps recognize anatomic variants and hippocampal pathology.The purpose of this pictorial review is threefold: (1) to review the normal anatomy of the hippocampus on MRI (2) to discuss the optimal imaging strategy for the evaluation of the hippocampus and (3) to present a pictorial overview of the most common anatomic variants and pathologic conditions affecting the hippocampus. The main indications requiring tailored imaging sequences of the hippocampus are medically refractory epilepsy and dementia.

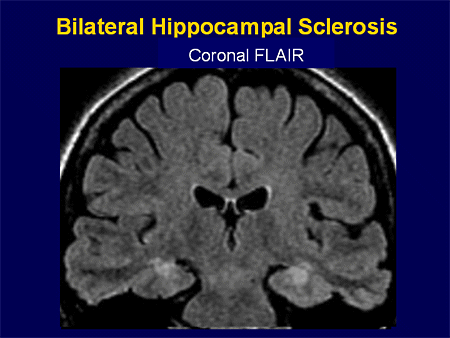
Magnetic resonance imaging is the preferred imaging technique for evaluating the hippocampus. In this lateral view of the human brain, the frontal lobe is at left, the occipital lobe at right, and the temporal and parietal lobes have largely been removed to reveal the hippocampus underneath. The hippocampus can be affected by a wide range of congenital variants and degenerative, inflammatory, vascular, tumoral and toxic-metabolic pathologies. Hippocampus 1 Hippocampus Brain: Hippocampus The hippocampus is located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. The hippocampus is a small but complex anatomical structure that plays an important role in spatial and episodic memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
